Subjective vs Objective Data in Nursing: Key Differences Explained
In the world of nursing, understanding the difference between subjective data and objective data is crucial for providing effective patient care. Subjective data refers to information based on a patient’s feelings, perceptions, and experiences, while objective data is measurable and observable, backed by evidence. Both types of data play a vital role in nursing assessments, but they serve distinct purposes. This blog will explore the key differences, importance, and practical applications of subjective vs objective data in nursing, ensuring you grasp the essentials for better patient outcomes. (nursing assessments, patient care, clinical decision-making)
What is Subjective Data in Nursing?

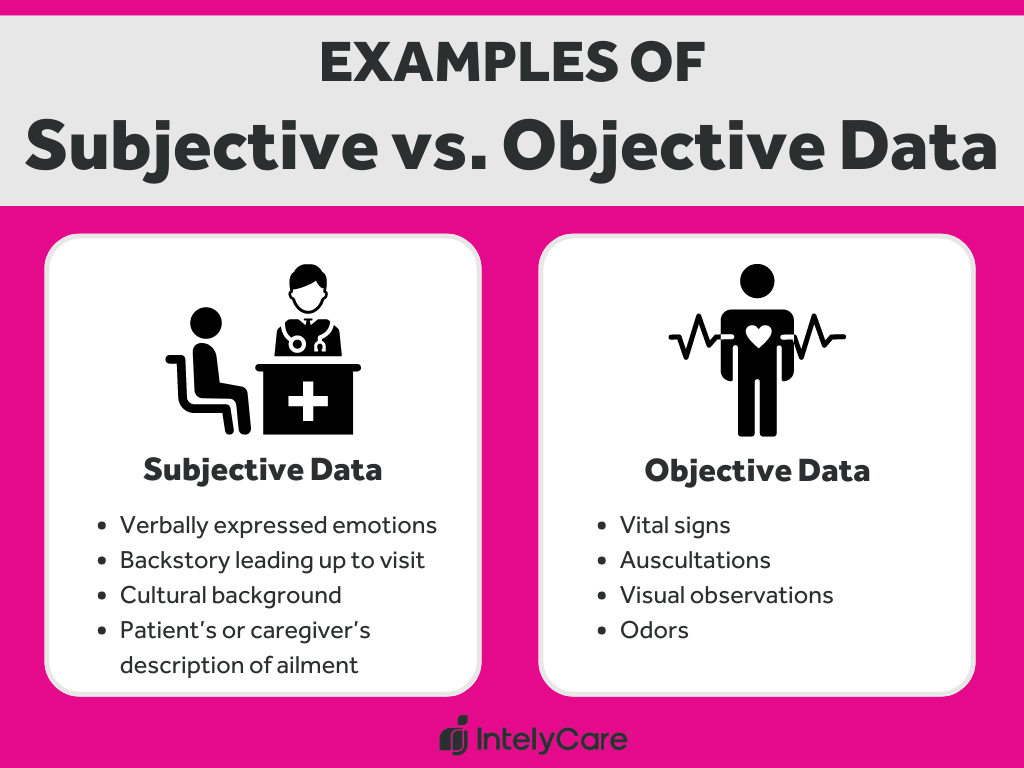
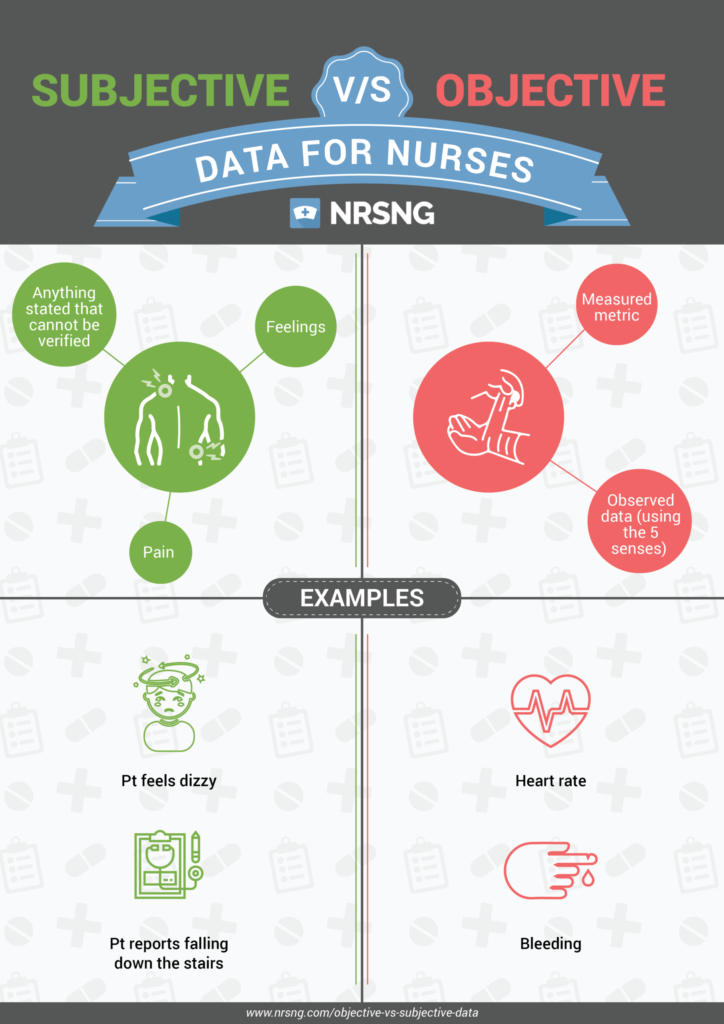
Subjective data is information gathered directly from the patient about their symptoms, feelings, and experiences. It is personal and cannot be measured or verified by a healthcare provider. Examples include pain levels, fatigue, nausea, or emotional distress. This type of data is essential because it provides insight into the patient’s perspective, which is critical for holistic care. (holistic care, patient perspective, symptom management)
Key Characteristics of Subjective Data
- Patient-Reported: Derived from the patient’s own words.
- Qualitative: Descriptive rather than numerical.
- Individualized: Varies from person to person based on perception.
💡 Note: Subjective data relies heavily on effective communication skills to accurately capture the patient’s experience.
What is Objective Data in Nursing?

Objective data, on the other hand, is factual and measurable. It includes vital signs, lab results, physical assessments, and other observable indicators. This data is verifiable and not influenced by personal feelings or opinions. Objective data forms the basis of clinical diagnoses and treatment plans. (clinical diagnoses, treatment plans, measurable outcomes)
Key Characteristics of Objective Data
- Measurable: Quantifiable and can be observed.
- Evidence-Based: Supported by tests, exams, or tools.
- Consistent: Less likely to vary between observers.
Comparing Subjective vs Objective Data

To better understand the differences, let’s compare the two in a table:
| Aspect | Subjective Data | Objective Data |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Patient’s self-report | Observable or measurable |
| Nature | Qualitative | Quantitative |
| Examples | Pain, fatigue, anxiety | Blood pressure, temperature, X-ray results |
| Reliability | Depends on patient’s perception | Consistent and verifiable |
Why Both Types of Data Matter in Nursing

Both subjective and objective data are indispensable in nursing practice. Subjective data helps nurses understand the patient’s emotional and psychological state, while objective data provides concrete evidence to support clinical decisions. Together, they create a comprehensive patient profile, enabling nurses to deliver personalized and effective care. (personalized care, comprehensive patient profile, clinical decisions)
Practical Applications
- Pain Management: Subjective data (patient’s pain description) combined with objective data (vital signs) guides pain management strategies.
- Diagnosis: Objective data (lab results) paired with subjective data (symptoms) aids in accurate diagnoses.
- Patient Education: Understanding both types of data helps nurses educate patients about their conditions and treatment plans.
📌 Note: Balancing subjective and objective data ensures a holistic approach to patient care.
Checklist for Gathering Subjective and Objective Data

To ensure you’re effectively collecting both types of data, use this checklist:
Subjective Data:
- Ask open-ended questions about symptoms and feelings.
- Listen actively and validate the patient’s experience.
- Document responses accurately in the patient’s own words.
- Ask open-ended questions about symptoms and feelings.
Objective Data:
- Perform thorough physical assessments.
- Record vital signs and lab results.
- Use tools like stethoscopes, thermometers, and blood pressure monitors.
- Perform thorough physical assessments.
In summary, subjective and objective data are two sides of the same coin in nursing. While subjective data provides insight into the patient’s personal experience, objective data offers measurable evidence to support clinical decisions. Mastering the collection and interpretation of both types ensures nurses can deliver holistic, patient-centered care. By understanding these differences, nursing professionals can enhance their practice and improve patient outcomes. (patient-centered care, nursing practice, improved outcomes)
What is the main difference between subjective and objective data?
+
Subjective data is based on the patient’s feelings and perceptions, while objective data is measurable and observable.
Why is subjective data important in nursing?
+
Subjective data provides insight into the patient’s emotional and psychological state, which is crucial for holistic care.
Can objective data exist without subjective data?
+
While objective data can exist independently, combining it with subjective data provides a more comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition.



